This press release is shared jointly with the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) and NSF’s NOIRLab. It first appeared in the IAS newsroom.
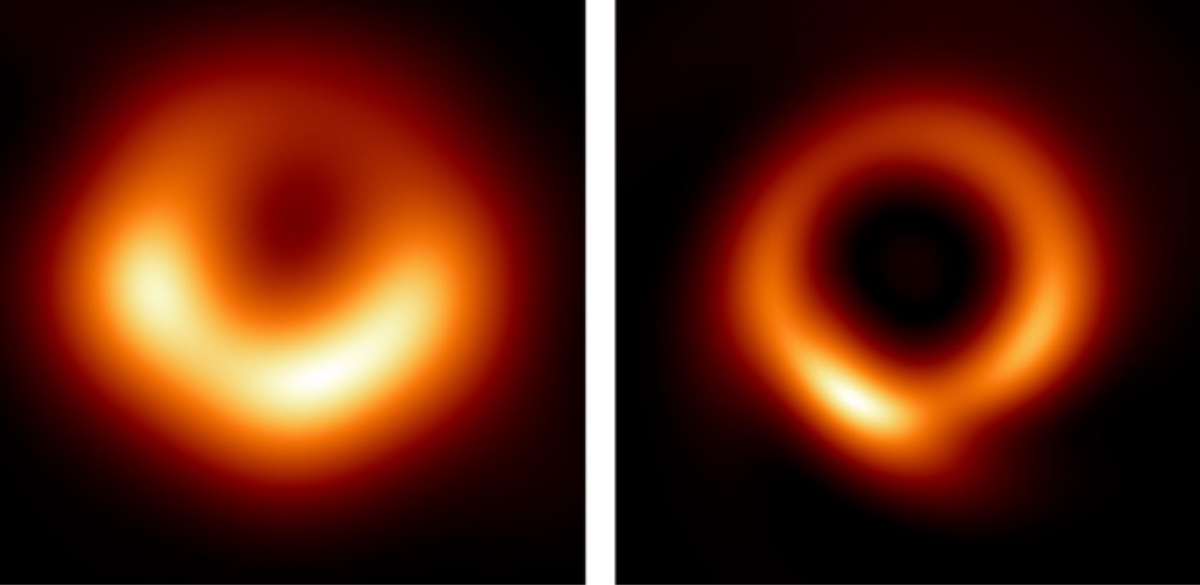
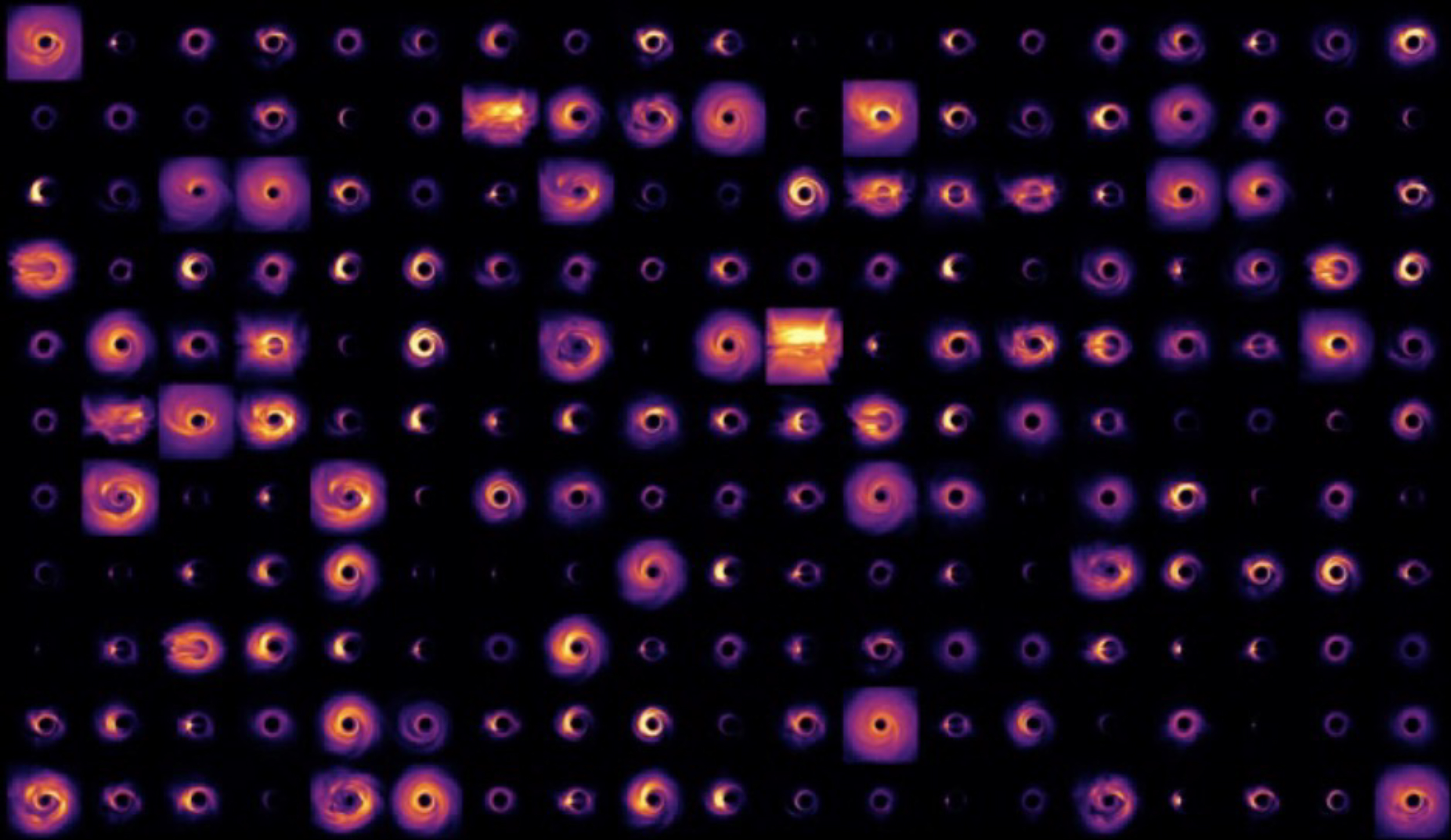
A team of researchers, including astrophysicists from Georgia Tech, the Institute for Advanced Study, and NSF’s NOIRLab, has developed a new machine-learning technique to enhance the fidelity and sharpness of radio interferometric images. To demonstrate the power of their new approach, which is called PRIMO, the team created a new, high-fidelity version of the iconic Event Horizon Telescope's image of the supermassive black hole at the center of Messier 87, a giant elliptical galaxy located 55 million light-years from Earth.
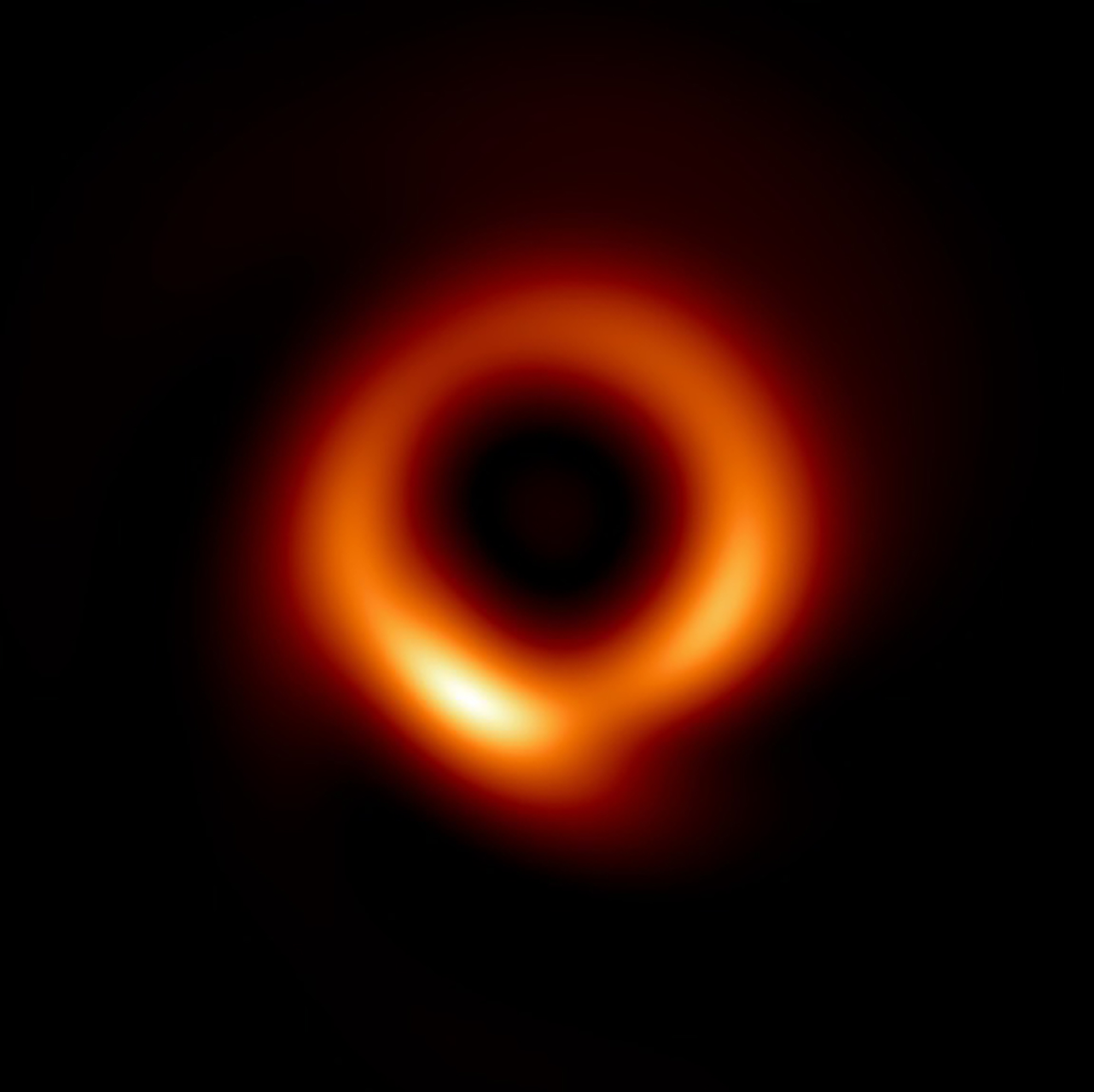
The iconic image of the supermassive black hole at the center of M87—sometimes referred to as the “fuzzy, orange donut”—has gotten its first official makeover with the help of machine learning. The new image further exposes a central region that is larger and darker, surrounded by the bright accreting gas shaped like a “skinny donut.” The team used the data obtained by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration in 2017 and achieved, for the first time, the full resolution of the array.
“The new image of the M87 black hole showcases the remarkable power of the highest-resolution telescope on Earth working in tandem with modern machine learning algorithms; it demonstrates how technology continues to push the boundaries of our understanding of the universe,” said Feryal Özel, professor and chair of the School of Physics at Georgia Tech.
In 2017, the EHT collaboration used a network of seven pre-existing telescopes around the world to gather data on M87, creating an “Earth-sized telescope.” However, since it is infeasible to cover the Earth’s entire surface with telescopes, gaps arise in the data—like missing pieces in a jigsaw puzzle.
“With our new machine learning technique, PRIMO, we were able to achieve the maximum resolution of the current array,” says lead author Lia Medeiros of the Institute for Advanced Study. “Since we cannot study black holes up-close, the detail of an image plays a critical role in our ability to understand its behavior. The width of the ring in the image is now smaller by about a factor of two, which will be a powerful constraint for our theoretical models and tests of gravity.”
PRIMO, which stands for principal-component interferometric modeling, was developed by EHT members Lia Medeiros (Institute for Advanced Study), Dimitrios Psaltis (Georgia Tech), Tod Lauer (NOIRLab), and Feryal Özel (Georgia Tech). Their publication, “The Image of the M87 Black Hole Reconstructed with PRIMO,” is now available in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
“PRIMO is a new approach to the difficult task of constructing images from EHT observations,” said Lauer. “It provides a way to compensate for the missing information about the object being observed, which is required to generate the image that would have been seen using a single gigantic radio telescope the size of the Earth.”
PRIMO relies on dictionary learning, a branch of machine learning which enables computers to generate rules based on large sets of training material. For example, if a computer is fed a series of different banana images—with sufficient training—it may be able to determine if an unknown image is or is not a banana. Beyond this simple case, the versatility of machine learning has been demonstrated in numerous ways: from creating Renaissance-style works of art to completing the unfinished work of Beethoven. So how might machines help scientists to render a black hole image? The research team has answered this very question.
With PRIMO, computers analyzed over 30,000 high-fidelity simulated images of black holes accreting gas. The ensemble of simulations covered a wide range of models for how the black hole accretes matter, looking for common patterns in the structure of the images. The various patterns of structure were sorted by how commonly they occured in the simulations, and were then blended to provide a highly accurate representation of the EHT observations, simultaneously providing a high fidelity estimate of the missing structure of the images. A paper pertaining to the algorithm itself was published in The Astrophysical Journal on February 3, 2023.
“We are using physics to fill in regions of missing data in a way that has never been done before by using machine learning,” added Medeiros. “This could have important implications for interferometry, which plays a role in fields from exo-planets to medicine.”
The team confirmed that the newly rendered image is consistent with the EHT data and with theoretical expectations, including the bright ring of emission expected to be produced by hot gas falling into the black hole. Generating an image required assuming an appropriate form of the missing information, and PRIMO did this by building on the 2019 discovery that the M87 black hole in broad detail looked as predicted.
“Approximately four years after the first horizon-scale image of a black hole was unveiled by EHT in 2019, we have marked another milestone, producing an image that utilizes the full resolution of the array for the first time,” stated Psaltis. “The new machine learning techniques that we have developed provide a golden opportunity for our collective work to understand black hole physics.”
The new image should lead to more accurate determinations of the mass of the M87 black hole and the physical parameters that determine its present appearance. The data also provides an opportunity for researchers to place greater constraints on alternatives to the event horizon (based on the darker central brightness depression) and perform more robust tests of gravity (based on the narrower ring size). PRIMO can also be applied to additional EHT observations, including those of Sgr A*, the central black hole in our own Milky Way galaxy.
M87 is a massive, relatively nearby, galaxy in the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Over a century ago, a mysterious jet of hot plasma was observed to emanate from its center. Beginning in the 1950s, the then new technique of radio astronomy showed the galaxy to have a compact bright radio source at its center. During the 1960s, M87 had been suspected to have a massive black hole at its center powering this activity. Measurements made from ground-based telescopes starting in the 1970s, and later the Hubble Space Telescope starting in the 1990s, provided strong support that M87 indeed harbored a black hole weighing several billion times the mass of the Sun based on observations of the high velocities of stars and gas orbiting its center. The 2017 EHT observations of M87 were obtained over several days from several different radio telescopes linked together at the same time to obtain the highest possible resolution. The now iconic “orange donut” picture of the M87 black hole, released in 2019, reflected the first attempt to produce an image from these observations.
“The 2019 image was just the beginning,” stated Medeiros. “If a picture is worth a thousand words, the data underlying that image have many more stories to tell. PRIMO will continue to be a critical tool in extracting such insights.”
Development of the PRIMO algorithm was enabled through the support of the National Science Foundation Astronomy and Astrophysics Postdoctoral Fellowship.
About Georgia Institute of Technology
The Georgia Institute of Technology, or Georgia Tech, is one of the top public research universities in the U.S., with more than 45,000 undergraduate and graduate students who study in person at the main campus in Atlanta, at Georgia Tech-Europe in France, at Georgia Tech-Shenzhen in China, as well as through distance and online learning. Students represent 50 states and more than 148 countries.
Georgia Tech's engineering and computing Colleges are the largest and among the highest-ranked in the nation, and the Institute also offers outstanding programs in business, design, liberal arts, and sciences.
With more than $1 billion annually in research awards across all six Colleges and the Georgia Tech Research Institute (GTRI), Georgia Tech is among the nation’s most research-intensive universities. It is an engine of economic development for the state of Georgia, the Southeast, and the nation.
Georgia Tech’s mission is to develop leaders who advance technology and improve the human condition. Its mission and strategic plan are focused on making a positive impact in the lives of people everywhere. Since 1885, the people of Georgia Tech have dared to imagine and then create solutions for a better future. The innovative culture and leadership continue — Progress and Service for all.
About the Institute for Advanced Study
The Institute for Advanced Study has served the world as one of the leading independent centers for theoretical research and intellectual inquiry since its establishment in 1930, advancing the frontiers of knowledge across the sciences and humanities. From the work of founding IAS faculty such as Albert Einstein and John von Neumann to that of the foremost thinkers of the present, the IAS is dedicated to enabling curiosity-driven exploration and fundamental discovery.
Each year, the Institute welcomes more than 200 of the world’s most promising post-doctoral researchers and scholars who are selected and mentored by a permanent Faculty, each of whom are preeminent leaders in their fields. Among present and past Faculty and Members there have been 35 Nobel Laureates, 44 of the 62 Fields Medalists, and 23 of the 26 Abel Prize Laureates, as well as many MacArthur Fellows and Wolf Prize winners.
For More Information Contact
Jess Hunt-Ralston
Georgia Institute of Technology
jess@cos.gatech.edu
(404) 385-5207
Lee Sandberg
Institute for Advanced Study
lsandberg@ias.edu
(609) 455-4398
Tod Lauer
NSF’s NOIRLab
tod.lauer@noirlab.ed